Components of a business plan
April 25, 2024 · 9 min read

The components of a business plan include key elements that outline the company’s products or services, target audience, financial forecasts, and organizational framework. The main components of a business plan are product, market, money, and people. The product component outlines the goods or services offered. The market component analyzes the target market and competition. The money component delves into financial projections and funding needs, while the people component discusses the management team and organizational structure.
The executive summary comes first in the business plan but it is written last, providing a concise overview of the entire document, while the appendix is last in a business plan, containing supplementary information.
Proper use of the components of a business plan is a key characteristic of a good business plan. A professional business plan has to have the appropriate components. The elements of a business plan dictate how a business plan is written. An experienced business plan consultant knows how to use the elements to make an outstanding business plan.
The following is a list of the parts of a business plan.

1. Executive Summary
The executive summary section of the business plan is a brief overview of the business, its goals, and how it plans to achieve them, highlighting the key points of the entire business plan. Executive Summary comes at the end and squeezes the main points into a short piece. It talks about the business idea, who it’s for, what makes it special, and how it’s expected to do financially.
The executive summary blends different parts to give a clear view of the business. It often includes a synopsis of the company’s objectives and mission, a list of the goods and services offered, a market analysis, and a peek at the competitors. It could also include a summary of the marketing strategy, noteworthy successes, and financial projections.
The executive summary section of the business plan is a strategic tool for attracting potential investors, partners, or stakeholders. It seeks to offer a thorough yet condensed synopsis that entices readers to study the plan in further depth. It is a strong introduction that lays the groundwork for additional research and analysis by condensing the company’s vision, strategy, and potential.

2. Company Description
Company Description is the detailed information about the business, including its name, location, mission, vision, and the products or services it offers. Consider a business plan’s company description as the organization’s “about me” section. The corporate description provides a comprehensive overview of a business’s history, goals, and future direction. This section aids readers in quickly understanding the main points of the company, providing a roadmap to comprehend its mission, similar to introducing oneself and the past.
A business plan’s company description is crucial since it serves as a potential lender, investor, and other influential people’s initial point of contact. Offering early insights into the company’s core values and background is akin to extending a warm and reassuring handshake. The company’s unique selling points and reasons for client preference are highlighted, providing an early glimpse into its exceptional qualities.
The company description sets the tone for the business plan, laying the foundation for subsequent sections. It serves as a beacon of guidance, bringing the reader’s comprehension into line with the goals and tactics of the organization. The business’s identity and aspirations are articulated, ensuring clarity and coherence in the plan, thereby creating a compelling narrative that resonates with stakeholders.
Company Description for Business Plan Example
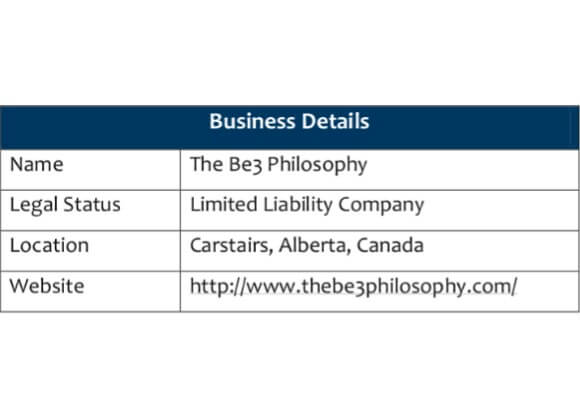
3. Vision and Mission
Vision is a forward-looking statement that outlines the business’s long-term aspirations and ultimate goal, outlining its future objectives and the impact it aims to have. A mission statement outlines the business’s core purpose, guiding daily operations and decision-making, outlining its activities, customers, and methods of service. The company’s main objectives, existence, and purpose are all outlined in the mission statement.
These components are essential to a company plan because they provide direction and clarity to all stakeholders, including consumers, investors, and staff. Inspired by the company’s ultimate goals and aspirations, the vision statement beacons the guidance for organizational alignment and strategic decision-making. The mission statement communicates the fundamental values, principles, and commitment to serve its stakeholders, encouraging confidence and allegiance.
A clear, concise vision and mission statements are crucial for a business plan to communicate the company’s beliefs and objectives effectively. The vision should be ambitious and achievable, motivating stakeholders to support a common purpose, while the mission should clearly state the company’s purpose, target audience, main services, and dedication to value. The statements form the foundation of the business proposal, providing a captivating narrative that outlines the company’s core and trajectory.
Vision and Mission in Business Plan Example

4. Business goals description
The business goal description section outlines measurable business objectives, such as financial targets, market expansion plans, product development milestones, customer acquisition metrics, and other key performance indicators (KPIs). These objectives serve as a roadmap, outlining the company’s strategic direction and acting as standards for success and advancement. They support the mission and vision of the business, assisting in directing choices and resource allocation.
Business goals are essential because they give the organization direction and clarity. Organizations can enhance work prioritization, resource allocation, and performance tracking by defining clear, measurable objectives. Well-defined objectives provide workers with a sense of direction and purpose, encouraging accountability and motivation.
A company strategy should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) to communicate and achieve goals effectively. Set goals that align with the organization’s mission, vision, long-term goals, and strategic priorities. The goals should also include progress and success measurements, given the resources and capabilities at hand, business goals ought to be reasonable and attainable.
5.Products and Services description
In a business plan, the product and service description summarizes what the company offers to its target market including their unique features, benefits, and potential for success. A company can offer products, such as physical items, or services, which include non-tangible offerings like upkeep, assistance, or advice. This section is crucial as it outlines the company’s products, customer satisfaction, and problem-solving methods.
Product and service descriptions are needed for a business to effectively communicate its value proposition to potential partners, investors, and customers. The company’s distinct features, benefits, and strengths enable stakeholders to set it apart from other market competitors. A precise and convincing explanation of products and services boosts trust and credibility among stakeholders, demonstrating the company’s knowledge and ability to deliver value.
A comprehensive business plan should outline every product or service, highlighting their attributes, capabilities, and details, to accurately present what is being offered. It highlights how the products or services can meet the target market’s needs and challenges, focusing on their value proposition and competitive edge. Incorporate pricing tactics, distribution networks, and upcoming product/service advancement plans to give a holistic perspective of the company’s offerings and expansion strategy.
6. Management and organizational structure
The management and organizational structure section describes the business’s organizational structure, ownership, and management team. It includes biographies of key executives and their roles. It identifies the main individuals handling decision-making, strategic planning, and daily activities. This part is essential as it showcases the skill and expertise of the leadership group, which is frequently a key element in a company’s prosperity.
The significance of the management and organizational structure is in assuring stakeholders like investors and lenders regarding the company’s effective execution of its business plan. The business plan boosts confidence in the leadership’s capabilities by giving information on the management team’s backgrounds, skills, and roles to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth. An established organizational framework aids in defining authority lines, communication paths, and duties within the business, promoting effectiveness and responsibility.
A business plan should include biographies or resumes of key executives and management team members, outlining their backgrounds, skills, and contributions to the business and its structure. Clearly state each employee’s responsibilities and roles, emphasizing how their leadership and expertise will advance the organization’s objectives. The corporation’s organizational structure, which includes committees, advisory boards, and outside experts, shows that a robust support network is in place.
7. Market research and analysis
Conducting market research and analysis involves a comprehensive understanding of the industry, target market, and market conditions, aiming to identify opportunities and challenges within the market landscape. Businesses can tailor their goods, services, and marketing strategies by using them to help them identify market trends, client needs, and rival companies. Through the early identification of advantages and potential obstacles, market research evaluates the viability of business ideas and expansion plans.
To conduct market research, target markets, rivals, industry trends, and consumer preferences information must be gathered, examined, and evaluated. Data that supports the formulation of strategic decisions and the execution of business strategies is collected using various research techniques. This process enables the company to understand market conditions, find opportunities, manage risks, and develop successful marketing strategies.
A thorough presentation of the target market’s size, growth potential, demographics, and purchasing patterns is essential in a business plan to integrate market research and analysis into the strategy. Investigate rival firms, market trends, and legal aspects that could influence the company’s operations and potential for growth. To confirm market assumptions and bolster your market analysis, ensure data from primary and secondary research sources such as surveys, interviews, market reports, and trade journals.
8. Competition Analysis
Competition analysis evaluates the business’s competitors, assessing their strengths, weaknesses, market share, pricing, products, and strategies, to help differentiate and develop competitive advantages. It describes the primary individuals in charge of decision-making, strategic guidance, and daily activities. This part is essential because it shows how skilled and knowledgeable the management team is, which is frequently a key element in a business’s success.
The management and organizational structure ensures the company executes its business plan for stakeholders like investors and lenders. The business plan fosters confidence in leadership’s ability to overcome challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve growth by providing detailed information about the management team’s backgrounds, skills, and roles. A well-defined organizational framework enhances a corporation’s effectiveness and accountability by establishing authority lines, communication channels, and duties.
Include the expertise, credentials, and contributions of important leaders and members of the management team in their bios or resumes. Give a clear explanation of their roles and how their experience will contribute to the company’s objectives. Give an overview of the corporate structure to emphasize the organization’s support network, including any committees, advisory boards, and outside consultants.
9. Market and Sales strategy
The market and sales strategy is a detailed strategy for attracting and converting customers into paying clients, encompassing marketing, sales, distribution channels, pricing, and customer retention initiatives. It entails a thorough strategy that combines market research results with detailed sales techniques and promotional efforts. This part outlines how the company plans to reach its revenue targets and build a strong presence in the market.
A business plan’s market and sales strategy connects a company’s products and services to its target audience. An organization can identify its target market segments, comprehend their needs and preferences, and develop tailored marketing messages and sales pitches with the aid of a clearly defined market and sales strategy. The system offers a structure for allocating resources, establishing goals for sales, and evaluating marketing and sales accomplishments, guaranteeing congruence with extensive corporate objectives.
A business plan must specify the company’s position within each target market segment and the target market segments to include a market and sales strategy. Provide various marketing strategies to effectively engage with the target audience, such as public relations, social media, online marketing, and advertising. The company plans to achieve its financial targets and expand by presenting a sales projection, detailing the sales process, including lead generation, customer acquisition, and conversion strategies.
10. Funding Request
The funding request section details the required funding, purpose, proposed terms, usage, and expected return on investment for external financing for a business, including product development, marketing, and hiring. Well-defined financial plans and projected returns can attract investors and lenders, helping the business secure capital for growth. An organized request boosts investor confidence by showing the company’s financial expertise and strategic planning.
A business plan should contain a comprehensive funding proposal that specifies the necessary sum and its intended use. Understanding the company’s financial situation, including income, expenses, and cash flow estimates, is essential for the fundraising proposal. The proposal should provide details on financing or investment characteristics like interest rate, collateral, payback conditions, and ownership participation to enhance transparency with potential lenders or investors.
The funding request describes the company’s requirements for capital and asks possible lenders or investors for money. It provides information about the necessary money, its goal, and its intended usage. Investors read this section to grasp the company’s financial needs and possible investment opportunities.
11. Financial Analysis and Forecast
Financial analysis involves detailed projections of a business’s financial performance, including income, cash flow, balance sheets, and break-even analysis, to assess its viability and sustainability over three to five years. The procedure includes analyzing previous financial documents, making educated forecasts about upcoming patterns, and anticipating the financial path of the company. This part of a business plan is vital because it offers lenders and investors essential details on the company’s financial status, possible expansion, and investment credibility.
Analyzing finances and predicting future outcomes are essential in determining a company’s ability to reach its goals and sustain financial health. Companies can showcase their understanding of financial acumen, marketing, and efficiency by presenting thorough future forecasts. Monitoring finances helps companies identify potential risks and growth opportunities, enabling informed decisions for long-term success.
A thorough financial analysis is necessary for a business plan including income, balance, and cash flow statements. The project aims to forecast the company’s cash flow, expenses, and revenue for the upcoming years. It requires a detailed explanation of the method and anticipated financial impact.
12. Recommendations
Recommendations in a business plan section offer strategic advice based on market research, competition analysis, and financial analysis, recommending areas like product development, market entry strategies, pricing adjustments, marketing campaigns, operational improvements, and risk management. They come from studying the business carefully, looking at things like the market, how things are done, and money matters. These recommendations are important because they give the company a clear plan for making growth changes in the long run.
These recommendations are essential because they translate all of the planning and research from the business plan into practical steps that can help the firm succeed. Clear and actionable advice helps the business stay focused on its strengths, address issues as they arise, seize expansion opportunities, and steer clear of potentially dangerous situations. They also facilitate consensus among all corporate stakeholders regarding the next course of action.
Selecting recommendations for a business plan that align with the company’s objectives and are feasible is crucial. The recommendations should be precise, quantifiable, and time-bound, outlining step-by-step implementation and outlining the success criteria. It’s also critical to consider how these concepts will impact other corporate operations, including hiring, money management, product sales, and operations management.
13. Appendix
The appendix in a business plan is supplementary information that supports the business plan, such as resumes of the management team, product images, legal documents, and other pertinent data. The plan’s key ideas may not be essential, but it contains additional information that investors or other interested parties may find intriguing. This section is crucial as it allows readers to delve deeper into specific subjects.
An appendix lends credibility and legitimacy to the main body of the business plan, which is why it’s crucial. Supplementary documents like market research reports, financial statements, or stakeholder resumes validate and enhance the credibility of the main plan’s information. It also enables readers to take note of the company’s goals, operations, and financial performance.
Putting everything in a logical and accessible order is crucial when producing an appendix for a business plan. Create an appendix list with numbered items for easy reference in the main plan, adding only necessary details to support the primary arguments. For comprehension, ensure each paper is appropriately labeled, arranged, and described.
Are the elements of a business plan similar to the characteristics of a good business plan?
No, the elements of a business plan are different from the characteristics of a good business plan. Several essential characteristics set a solid business plan apart from a simple list of required elements. It should provide a thorough but targeted summary of the company’s objectives, plans, and financial projections. It should be clear, concise, and reasonable. A strong business strategy is thoroughly investigated, strategically sound, and flexible enough to adjust to shifting market conditions. It should engage and persuade readers, presenting the company’s vision and potential compellingly and professionally. A strong business plan does more than just list components. It embodies these qualities to persuade stakeholders of the company’s worth and potential.
Do all types of business plans contain the same components?
No, all business plan types are created differently since some components may be more meaningful in one type than in another. A new business plan for a startup has a format comparable to other business plans. It provides a comprehensive overview of the company, including a summary for executives, market analysis, marketing strategy, operations plan, management structure, financial projections, and appendices. This applies regardless of the company’s size or industry. The core components of business plans are consistent, although they may vary in complexity and detail depending on the company’s requirements and objectives. This uniform framework simplifies thorough business assessment, allowing stakeholders to make knowledgeable decisions and evaluate the sustainability of the project
How do the components affect how to write a business plan?
The process of creating a business plan involves a step-by-step approach. Each component plays a crucial role in directing the process. Every aspect, starting from the summary of the executives to the financial forecasts, offers an organized layout for structuring and showcasing important details regarding the company. Entrepreneurs can guarantee that every crucial aspect of their business is thoroughly and cohesively addressed by adhering to the outline offered by these components. Moreover, the elements assist authors in honing their research endeavors and collecting pertinent information and perspectives to back their analysis and suggestions. The elements of a business plan guide authors, leading them through creating a thorough and successful plan that conveys the business’s vision, strategy, and potential.
How does a professional business plan writer apply components of a business plan?
A professional business plan writer utilizes a specific structure to ensure that all key elements, from the executive summary to the financial analysis, are included and addressed thoroughly. A professional business plan writer gathers business information, goals, target market, and competitive landscape, then crafts a clear, concise, and tailored plan. They incorporate data, research findings, and industry insights to communicate the vision, strategy, and potential of the business.
Hire business plan writers who create tailored plans for unique industry requirements. They focus on strategic frameworks and standard components, ensuring thoroughness and effectiveness. They also provide cost-effective services, quality, and collaboration, ensuring satisfaction.


